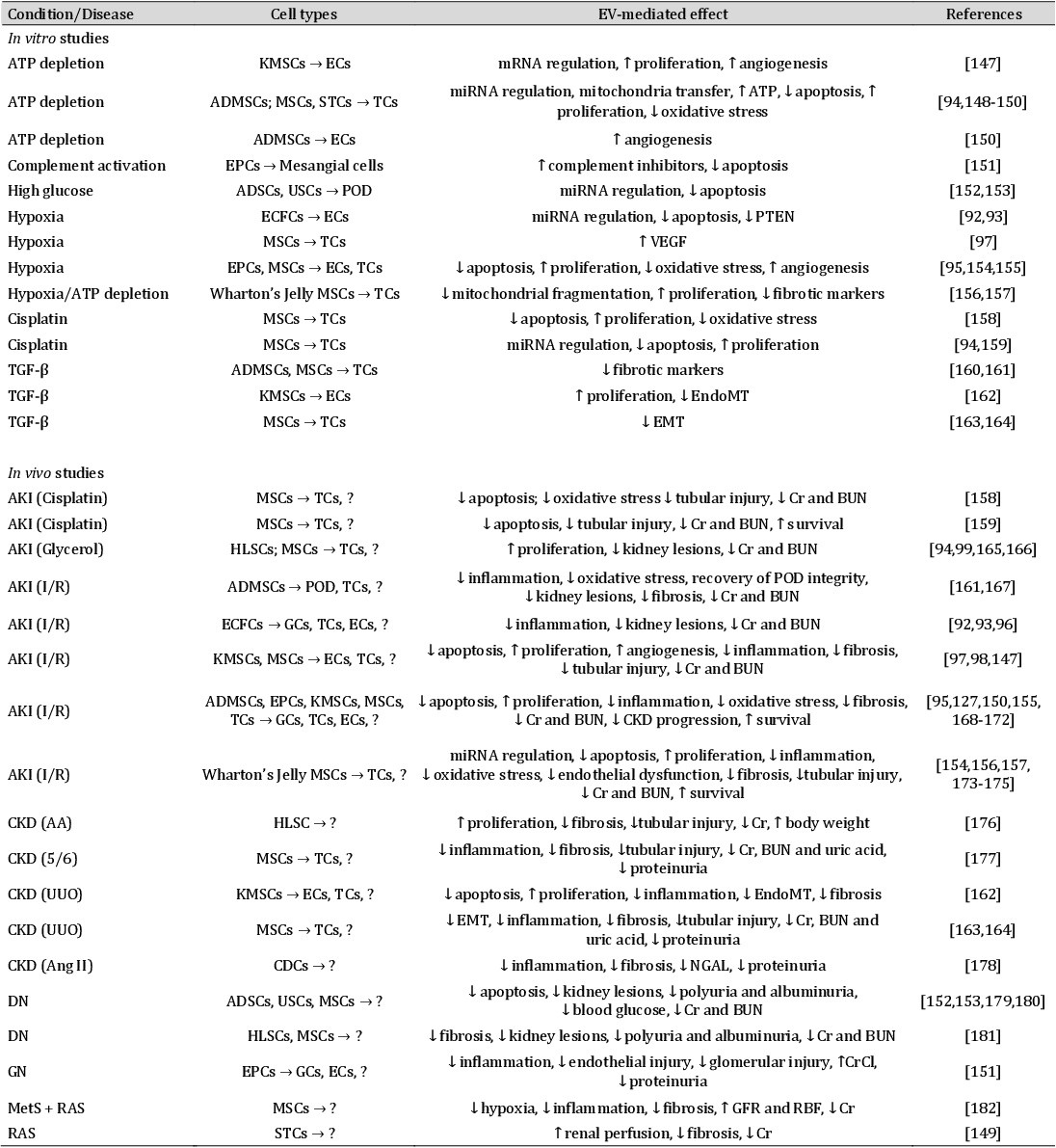
Table 2. Summary of studies investigating protective effects of extracellular vesicles in renal cellular recovery and kidney disease. Arrows indicate paracrine signaling promoted by EVs. AA = aristolochic acid; ADSCs = adipose-derived stem cells; ADMSCs = adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; AKI = acute kidney injury; Ang II = angiotensin II; BUN = blood urea nitrogen; CDCs = cardiosphere-derived cells; CKD = chronic kidney disease; Cr = creatinine (plasma or serum); CrCl = creatinine clearance; DN = diabetic nephropathy; ECs = endothelial cells; ECFCs = endothelial colony-forming cells; EMT = epithelial-mesenchymal transition; EndoMT = endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition; EPCs = endothelial progenitor cells; GCs = glomerular cells; GFR = glomerular filtration rate; GN = glomerulonephritis; HLSCs = human liver stem cells; I/R = ischemia-reperfusion; KMSCs = kidney mesenchymal cells; MetS = metabolic syndrome; MSCs = mesenchymal stromal cells; NGAL = neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; POD = podocytes; PTEN = phosphatase and tensin homolog; RAS = renal artery stenosis; RBF = renal blood flow; STCs = scattered-like cells; TCs = tubular cells; TGFβ = transforming growth factor β; USCs = urine-derived stem cells; UUO = unilateral ureter obstruction; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor